SPECIAL
CRIMES
Glosary
Particular
offenses: they
are crimes that affect legally protected life, physical integrity and
heritage
Special
crimes: they
are crimes that affect the common good and more besides that this
typified in the penal code; there is a special law, which punishes
criminal behavior
Murder:
action
consists of an omission by which is deprived of life to another
person either fraudulent or culpable
Genetic
manipulation: is
a procedure whose techniques can be used to benefit humanity or
illegal purposes. Making genetic manipulation is to modify the
genetic information and the flow of the species
Kidnapping:
it
is a crime that is deprived of illicitly liberty a person, usually
for a certain time, with the aim of obtaining a ransom or compliance
with other requirements to the detriment of the or abductors
Theft:
commits the offense of robbery without knowledge of who can legally
grant it, seizes a chattel alien
Fraud:
fraud is that a person obtains from another a benefit, is made of a
thing or profiteer after an error or by deception
WEAPONS
AND EXPLOSIVES
Weapon:
an
instrument or tool to attack or defend
Gun:
a
device to propel projectiles by one or multiplo pressure generated by
the combustion of a propellant
Ballistic
is the study of different projectiles used in firearms in this
discipline is analyzed weight, shape and size of a bullet
Useful
cartridge:
a set consisting of a metal or plastic container called a sheath or
cap
Ammo:
ammo
is the set of supplies needed to shoot guns
Projectile
is any object launched into space by the action of a force
Powder:
a
deflagrating substance mainly used as propellant missiles in
deflagrating substance mainly used as propellant missiles in firearms
Statistics:
it
is a reference to the harvest formal science, analysis, data
interpretation, either to assist in the resolution of the decision or
explain conditional regular or irregular conditions of some
phenomenon or applied study of occurrence of random or
Statistics
descriptive: it
is a big part of statistics that is dedicated to collect, sort,
analyze and represent a set of data in order to describe the
characteristics of this
Inferential
statistics: is
a part of statistics comprising the methods and procedures through
the induction of a population determines properties
Qualitative
variable:
those who do not have numerical values if not features or qualities
Quantitative
variable: those
are adopting numerical values
Absolute
frequency: the number of occurrences of a given value in a
statistical study
Relative
frequency:
the ratio of the absolute frequency of a certain value and the total
number of data can be expressed as a percentage and is represented by
(FR)
Cumulative
frequency:
is the sum of the absolute frequencies of all values less than or
equal to the value considered
CRIMINOLOGY
ADDRESSES
Criminology:
is a synthetic, casual, explanatory, natural and cultural science of
anti-social behavior
Criminology
psychology:
the study of the soul of the criminal subject
Criminal
policy: is considered as the study of the set of measures used by the
organs of government, to tackle crime affecting a state, with the
intention of finding relevant solution in reducing crime levels
respecting the rule of law
Mechanical
prevention:
try to create obstacles than will close the road to crime
Punitive
prevention: based on the intimation of withdrawal by criminal threat
Collective
prevention:
try to detect and remove if a criminological factor is possible in
life
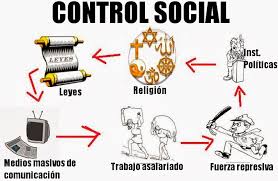
SOCIAL
CONTROL THEORY
Social
control:
is the set of practices, activities and values, to maintain the
established order in society
Anomie:
lack of standards or inability to foresee the social structure of
certain individuals what is necessary to achieve the goals of society
Prison
system: is
the term that is designated to institution or the system established
for compliance with the penalties provided in judicial decisions;
especially imprisonment, whose purpose is the social rehabilitation
of the convicted
Human
rights: inherent
to all human beings, without distinction of nationality, place of
residence, sex, national or technical origin, color, religion,
language or any other condition. We all have the same human rights
without discrimination
Formal
control:
the one that comprise the state institutions such as for example the
police, judges in the administration of justice or the prison
administration
Informal
control:
the one that appears in the society itself and therefore is a control
that comes from the family, the education received in school and the
office of the profession each person
THEORY
OF CRIMINAL PROCEEDINGS
Criminal
proceedings: is
known as stages and cases within them to follow the court case by the
commission of an offense under penal code.
Presumption
of Fragrance:
when wing person who performed the criminal act charged and is
possession of the stolen object.
Evidence:
is the clear and manifest certainty of a thing so that nobody can
doubt it.
Test:
it
is the necessary activity that involves demonstrating the truth of a
fact.
Hint:
it’s
all significant sensitive material that can be perceived through the
senses and that is in relation to the criminal incident under
investigation.
Protective
orders: restitution
of the victim to ensure the repair of damage